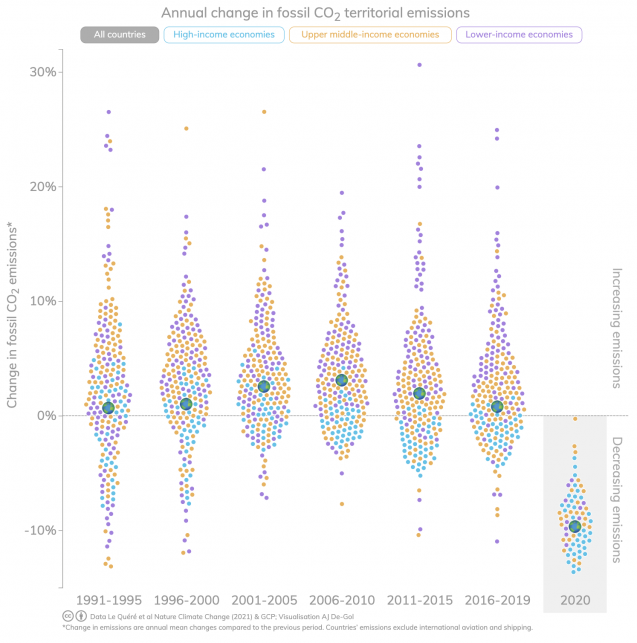
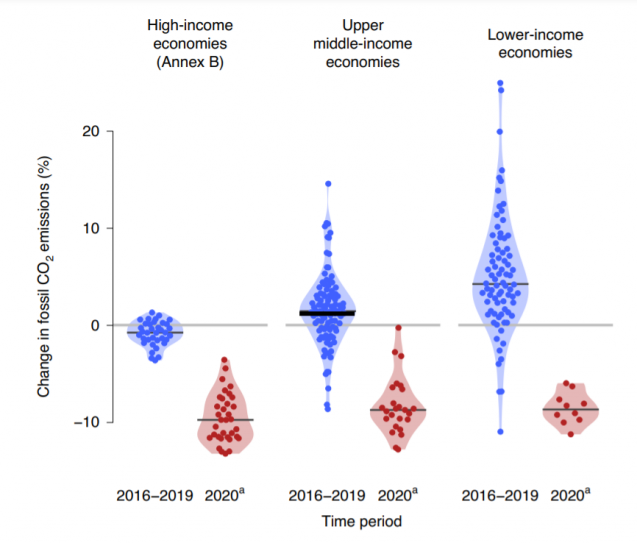
New research supported by 4C shows 64 countries cut their fossil CO2 emissions during 2016-2019, but the rate of reduction needs to increase tenfold to meet the Paris Agreement aims to tackle climate change.
This first global stocktake by researchers at the University of East Anglia (UEA), Stanford University and the Global Carbon Project examined progress in cutting fossil CO2 emissions since the Paris Agreement was adopted in 2015. Their results show the clear need for far greater ambition ahead of the important UN climate summit in Glasgow in November (COP26).
The annual cuts of 0.16 billion tonnes of CO2 are only 10% of the 1-2 billion tonnes of CO2 cuts that are needed globally every year to tackle climate change.
“Countries’ efforts to cut CO2 emissions since the Paris Agreement are starting to pay off, but actions are not largescale enough yet and emissions are still increasing in too many countries,” said Prof Corinne Le Quéré, Royal Society Professor at UEA’s School of Environmental Sciences, who led the analysis.
While emissions decreased in 64 countries, they increased in other 150 countries. Globally, emissions grew by 0.21 billion tonnes of CO2 per year during 2016-2019 compared to 2011-2015.
The scientist’s findings, ‘Fossil CO2 emissions in the post-COVID era’, have been published in Nature Climate Change. The study has been supported by the European Commission Horizon 2020 4C project.
Fig. 1 | Screenshoot of the interactive data visualisation created by Anthony De-Gol showing the latest emissions figures comparing country by country progress with their CO2 emissions. The application is available in https://enactivescience.com/gcp/.
Disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic
In 2020, confinement measures to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic cut global emissions by 2.6 billion tonnes of CO2, about 7% below 2019 levels. The researchers say 2020 is a ‘pause button’ that cannot realistically continue while the world overwhelmingly relies on fossil fuels, and confinement policies are neither a sustainable nor desirable solution to the climate crisis.
“The drop in CO2 emissions from responses to COVID-19 highlights the scale of actions and of international adherence needed to tackle climate change. Now we need large scale actions that are good for human health and good for the planet. It is everyone’s best interests to build back better and speed the urgent transition to clean energy,” said Prof Le Quéré.
The world has warmed by over 1 °C since the Industrial Revolution because of emissions of greenhouse gases from human activities. Annual cuts of 1-2 billion tonnes of CO2 are needed throughout the 2020s and beyond to avoid exceeding global warming within the range 1.5 °C to well below 2 °C, the ambition of the UN Paris Agreement.
Key role of climate change laws and policies
The growing number of climate change laws and policies appears to have played a key role in curbing the growth in emissions during 2016-2019. There are now more than 2000 climate laws and policies worldwide.
Of the 36 high income countries, 25 saw their emissions decrease during 2016-2019 compared to 2011-2015, including the USA (-0.7% per year), the European Union (-0.9% per year), and the UK (-3.6% per year). Emissions decreased even when accounting for the carbon footprint of imported goods produced in other countries.
Thirty of 99 upper-middle income countries also saw their emissions decrease during 2016–2019 compared to 2011–2015, suggesting that actions to reduce emissions are now in motion in many countries worldwide. Mexico (-1.3% per year) is a notable example in that group, while China’s emissions increased 0.4% each year on average, much less than the 6.2% annual growth of 2011-2015.
“The growing commitments by countries to reach net zero emissions within decades strengthens the climate ambition needed at COP26 in Glasgow. Greater ambition is now backed by leaders of the three biggest emitters: China, the United States, and the European Union,” said Prof Rob Jackson of Stanford University, who co-authored the study.
Green pandemic recovery is essential
A full bounce-back in 2021 to previous CO2 emission levels appears unlikely. However, the authors say unless the COVID-19 recovery directs investments in clean energy and the green economy, emissions will likely start increasing again within a few years.
The nature of the disruption in 2020, particularly affecting road transport, means incentive to expedite the large-scale deployment of electric vehicles and encourage walking and cycling in cities are timely and would also improve public health. The resilience of renewable energy throughout the crisis, falling costs, and air quality benefits, are additional incentives to support their large-scale deployment.
Investments post-COVID continue to be overwhelmingly dominated by fossil fuels in most countries, in contradiction with climate commitments, including in the United States and China. The European Union, Denmark, France, the United Kingdom, Germany and Switzerland are among the few countries that have so far implemented substantial green stimulus packages with limited investments in fossil-based activities.
“Countries need to align post-COVID incentives with climate targets this decade, based on sound science and credible implementation plans,” said Prof Jackson.
Prof Le Quéré added: “This pressing timeline is constantly underscored by the rapid unfolding of extreme climate impacts worldwide.”
See the latest emissions figures comparing country by country progress with their CO2 emissions (application created by Anthony De-Gol at UEA): https://enactivescience.com/gcp/
Study: Corinne Le Quéré C., Peters G., Friedlingstein P. et al. (2021). Fossil CO2 emissions in the post-COVID era. Nature Climate Change. DOI: 10.1038/s41558-021-01001-0