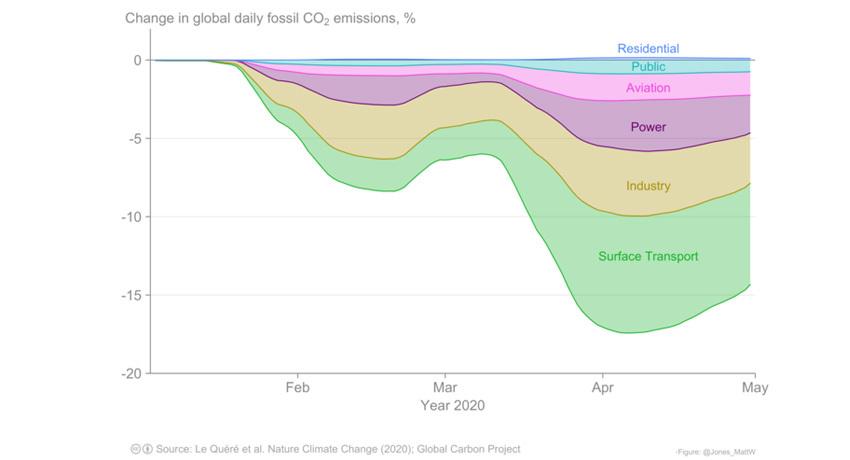
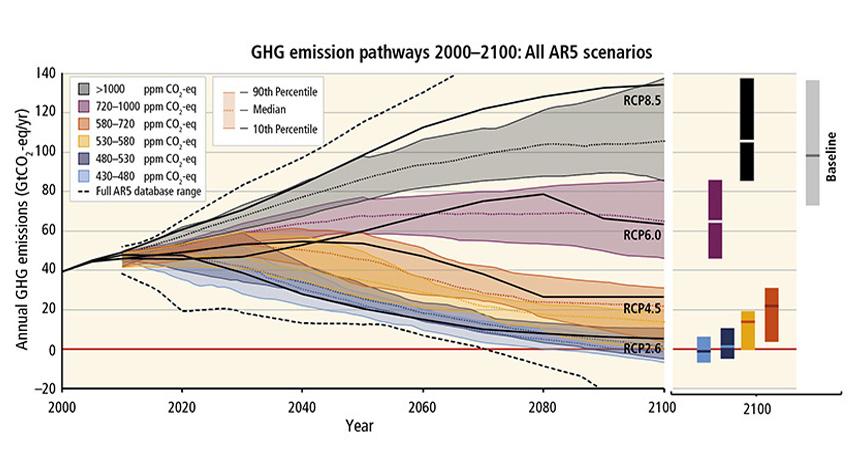
Virtual Emergent Constraints and Tipping Points Workshop 23 26 November 2020
These collaborative workshops bring together Climate Scientists, Mathematicians and Ecologists to answer key questions around the relationships between the variability and sensitivity of the Earth System and its subcomponents.
The first workshop will discuss proposed emergent constraints on future projections, many of which are based-on assumed relationships between sensitivity and variability.