The European Commission brings together the Earth System Science Horizon 2020 projects and policy makers to exchange knowledge and needs.
An updated review published on ScienceBrief strengthens the evidence that human-induced warming increases the frequency and severity of fire weather, which leads to more extreme fire seasons.
Short-term variations in atmospheric CO2 levels are caused by natural processes or human activities. This classroom discusses these drivers to better understand what affects changes in CO2 levels and why this is relevant for the political agenda.
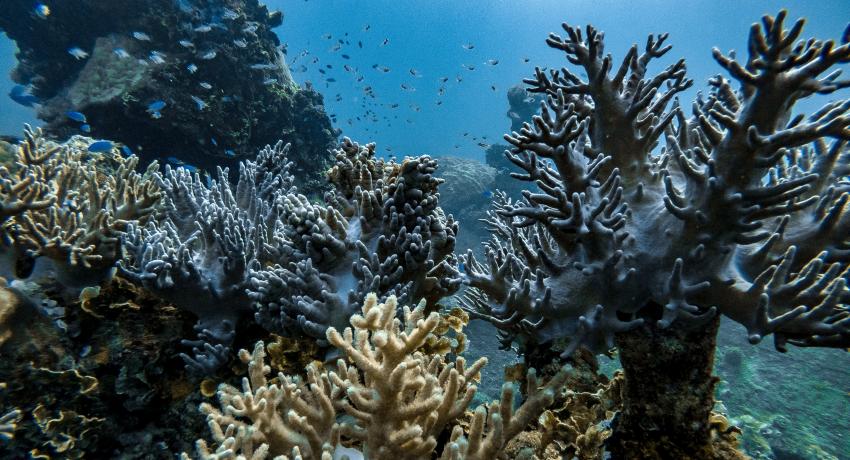
According to a new study published in Nature, Arctic Ocean acidification over the 21st century, mainly caused by the uptake of anthropogenic CO2 by the ocean, is projected to be greater than previously estimated. Ocean acidification threatens the life of calcifying organisms, such as corals and shellfish, and can have serious consequences for the entire food chain.
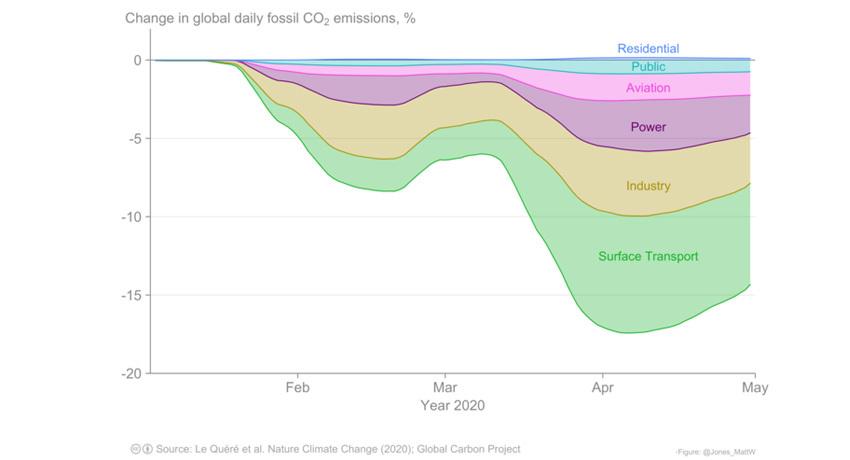
A study led by 4C scientists estimates a 17% decrease in CO2 emissions at the peak of the COVID-19 forced confinement. However, this temporary decrease in emissions cannot be sustained without structural changes in the economic recovery policies.
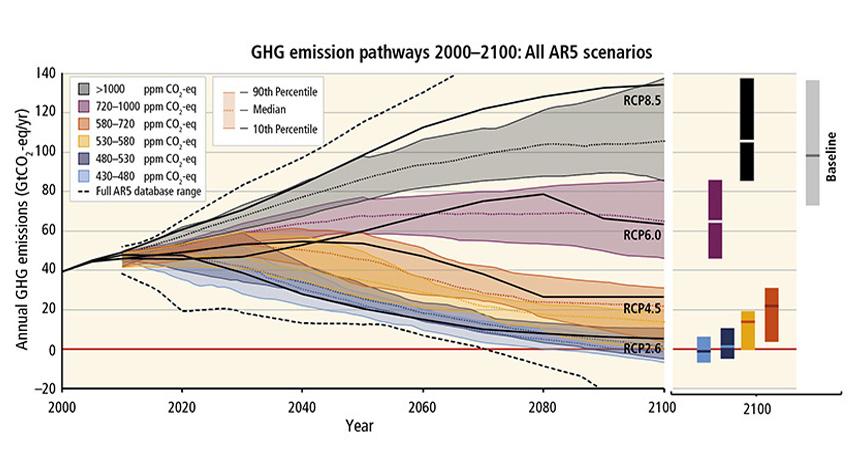
A workshop was held during the 4C kick-off meeting to discuss the potential contributions of 4C to the Sixth Assessment Report of IPCC.
The Climate-Carbon Interactions in the Current Century (4C) project holds kick-off meeting in June 2019.